Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
- Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Jeong-Ju Yoo
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):189-201. Published online March 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.03.11
- 1,593 Views
- 65 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
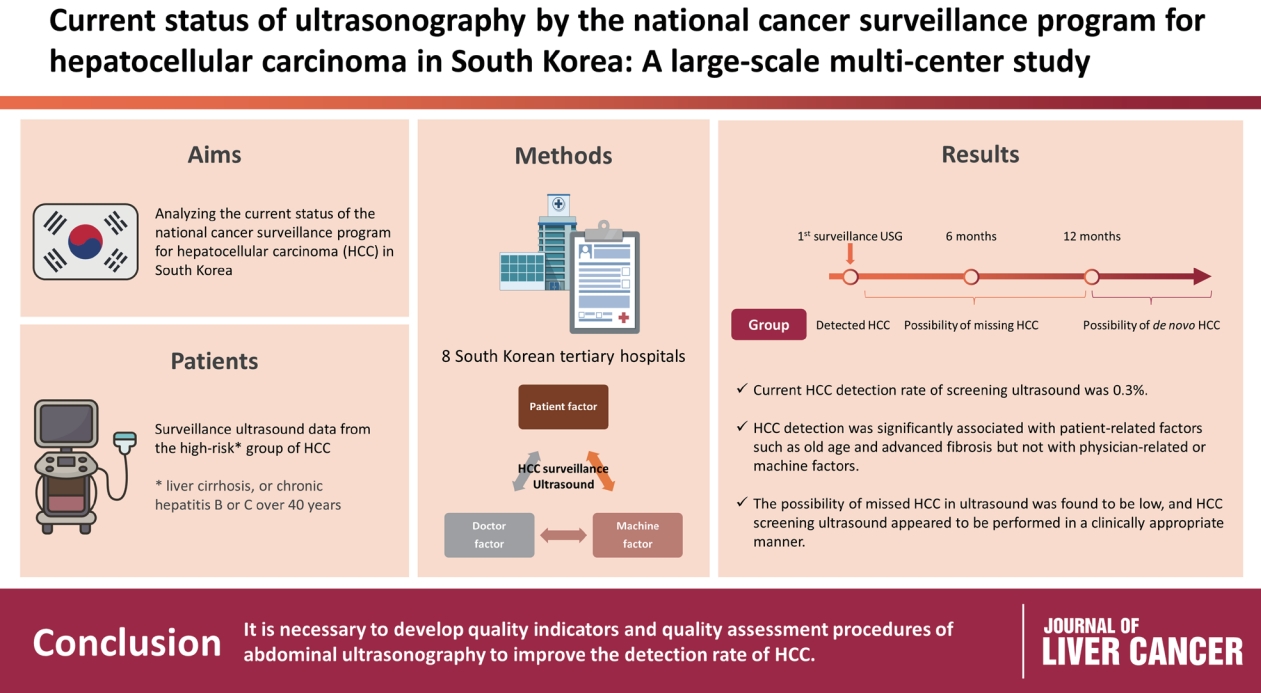
Abdominal ultrasonography (USG) is recommended as a surveillance test for high-risk groups for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to analyze the current status of the national cancer surveillance program for HCC in South Korea and investigate the effects of patient-, physician-, and machine-related factors on HCC detection sensitivity.
Methods
This multicenter retrospective cohort study collected surveillance USG data from the high-risk group for HCC (liver cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B or C >40 years of age) at eight South Korean tertiary hospitals in 2017.
Results
In 2017, 45 experienced hepatologists or radiologists performed 8,512 USG examinations. The physicians had a mean 15.0±8.3 years of experience; more hepatologists (61.4%) than radiologists (38.6%) participated. Each USG scan took a mean 12.2±3.4 minutes. The HCC detection rate by surveillance USG was 0.3% (n=23). Over 27 months of follow-up, an additional 135 patients (0.7%) developed new HCC. The patients were classified into three groups based on timing of HCC diagnosis since the 1st surveillance USG, and no significant intergroup difference in HCC characteristics was noted. HCC detection was significantly associated with patient-related factors, such as old age and advanced fibrosis, but not with physician- or machine-related factors.
Conclusions
This is the first study of the current status of USG as a surveillance method for HCC at tertiary hospitals in South Korea. It is necessary to develop quality indicators and quality assessment procedures for USG to improve the detection rate of HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels
Soon Kyu Lee, Soon Woo Nam, Jeong Won Jang, Jung Hyun Kwon
Diagnostics.2024; 14(5): 495. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

- An Analysis for Survival Predictors for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Failed to Sorafenib Treatment in Pre-regorafenib Era
- Chan Uk Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Minjin Lee, Sehwa Kim, Young Kul Jung, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):117-127. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.117

- 4,222 Views
- 64 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Sorafenib is the standard treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We aimed to investigate the prognosis predictors and the role of second-line cytotoxic systemic chemotherapy (CSC) in patients with advanced HCC after sorafenib discontinuation in the pre-regorafenib era.
Methods
From 2007 to 2015 in the pre-regorafenib era, the medical records of 166 HCC patients, who had permanently discontinued sorafenib, were retrospectively reviewed. For further analysis of survival factors after sorafenib treatment failure, we compared the survival of patients who had maintained liver function after second-line treatment with the best supportive care (BSC) group and selective BSC (SBSC) group.
Results
After discontinuation of sorafenib, median overall survival (OS) was 2.8 (1.9-3.7) months. The OS in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to adverse effect, progression, and poor clinical condition were 5.5 (2.4-8.6), 5.5 (2.2-8.9), and 0.9 (0.5-1.3) months, respectively (P<0.001). The independent predictive factors of survival after sorafenib failure were serum level of bilirubin and albumin, α-fetoprotein, discontinuation cause, and second-line CSC. In comparison with survival between second-line CSC and BSC group, the CSC group showed better survival outcome compared to the BSC group (10.6 vs. 1.6 months, P<0.001) and SBSC group (10.6 vs. 4.2 months, P=0.023).
Conclusions
The survival after sorafenib failure in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to progression and adverse effects was significantly better than in those who discontinued treatment due to clinical deterioration. In the pre-regorafenib era, patients who received second-line CSC showed better survival than those who received only supportive care after sorafenib failure.

Case Report
- A Case of Simultaneous Resection of Recurrent Combined Hepatocellular Cholangiocarcinoma and Hypovascular Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Tae Hyung Kim, Soon Ho Um, Sang Jung Park, Seung Woon Park, Han Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Dong Yu, Dong-Sik Kim, Joo Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):94-99. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.94
- 1,853 Views
- 11 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver cancer is more complex to treat compared to cancers in other organs, since liver function should be considered. In addition, only a few patients can be applied curative treatment due to advanced stage at diagnosis. Therefore, early stage detection is important and has been increased through screening and surveillance programs using image modalities recently. However, it is still difficult to diagnose small or hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) even using advanced image modalties. In particular, hypovascular HCCs do not show arterial contrast enhancement which is a typical finding of HCC on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Those also account for a considerable portion of early HCC. We present 54 yearsold man who had recurrent hypervascular and hypovascular nodules on three phase CT and gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. The nodules were removed by surgical resection and confirmed as combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and well differentiated HCC respectively.

Original Article
- Factors Affecting Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: Implications for Future Therapeutic Strategies
- Sang Jun Suh, Hyung Joon Yim, Dong Won Lee, Jong Jin Hyun, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Soon Ho Um
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):60-71. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.60
- 2,123 Views
- 23 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) exhibits poor prognosis. The aim of this study is to evaluate factors associated with survival of HCC patients with PVTT to suggest better therapeutic options.
Methods
Patients with HCC which were newly diagnosed at three tertiary hospitals between January 2004 and December 2012, were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, Barcelona Clinic of Liver Cancer stage C patients with PVTT were identified. Factors affecting overall survival (OS) were analyzed and efficacies of the treatment modalities were compared.
Results
Four hundred sixty five patients with HCC and PVTT were included. Liver function, tumor burden, presence of extrahepatic tumor, alfa fetoprotein, and treatment modalities were significant factors associated with OS. Treatment outcomes were different according to the initial modalities. OS of the patients who received hepatic resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), sorafenib, systemic cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation therapy (without combination), and supportive care were 27.8, 7.1, 6.7, 5.3, 2.5, 3.0, 1.8, and 0.9 months, respectively (P<0.001). Curative-intent treatments such as hepatic resection or RFA were superior to noncurativeintent treatments (P<0.001). TACE or HAIC was superior to sorafenib or systemic chemotherapy (P<0.001). Combining radiotherapy to TACE or HAIC did not provide additional benefit on OS (P=0.096).
Conclusions
Treatment modalities as well as baseline factors significantly influenced on OS of HCC patients with PVTT. Whenever possible, curative intent treatments should be preferentially considered. If unable, locoregional therapy would be a better choice than systemic therapy in HCC patients with PVTT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies
Keera Kang, Sung Kyu Song, Chul-Woon Chung, Yongkeun Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2020; 24(3): 243. CrossRef
- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies

Case Reports
- A Case of Management for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Lung Metastasis
- Han Jo Jeon, Tae Hyung Kim, Soon Ho Um, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyun Seo Kim, Ki Joon Lim, Seung Woon Park, Han Ah Lee, Dong-Sik Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):129-133. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.129
- 1,068 Views
- 14 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver cancer is the 2nd most common cause of cancer related death in Korea. Especially, patients who present extrahepatic spread of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have a shorter life expectancy (50% survival at 1 year and less than 4 months of median overall survival). Molecular target agent like sorafenib was usually mentioned as a treatment for them, but that was still not firmly established. We present a 75 year-old who had expanding nodular type of HCC. The mass was removed by resection and radiofrequency ablation. However, lung metastasis were revealed shortly after surgery. That lesions were treated with lenvatinib and systemic chemotherapy.

- Clinical Outcome of Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Single Session in Patients with Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis
- Min Seon Park, Soon Ho Um, Ho Sang Ryu, Yeon Seok Seo, Sun Young Yim, Chang Ho Jung, Tae Hyung Kim, Dae Hoe Gu
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):139-142. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.139
- 970 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) occur in the Asia-Pacific region and in patients with underlying hepatitis B and C viral infection. Although surgical resection is the gold standard for treatment of HCC, only a few patients are surgical candidates because of their lack of hepatic reserve. Liver transplantation, which eradicates HCC and replaces damaged noncancerous hepatic parenchyma, is regarded as the best treatment for HCC in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. However, the shortage of donors limit its widespread use. Furthermore, the long waiting time for liver transplantation allow for tumor progression and reduce patient survival. Given this long wait, there is a reasonable clinical need in the meantime for minimally invasive methods to avoid progression of HCC in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. We herein offer our experiences of therapeutic efficacy and complications of the procedure and the changes in liver function before and after TACE and radiofrequency ablation in patients with HCC and decompensated liver cirrhosis, defined as a Child-Pugh-Turcotte score above 7. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:139-142)

- Two Cases of Small (< 1 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jin Yong Jung, Sun Young Yim, Chang Ha Kim, Jin Dong Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Ho Sang Ryu, Min Ju Kim, Beom Jin Park, Soon Ho Um
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):37-41. Published online February 28, 2012
- 513 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tumor size is one of the most important factors for decision of therapeutic plan and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). If the diagnosis of HCC is made earlier in its small size, the prognosis is better. However the diagnosis of small HCC is not easy because small HCC lacks the typical clinical and radiologic feature. We experienced two cases of small HCC less than 1 cm that was confirmed after first treatment.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Early Multiple Recurrences after Liver Resection
- Jae Hong Ahn, Hyung Joon Yim, Seung Young Kim, Jeong Han Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Seung Hwa Lee, Hwan Hoon Chung, Tae Jin Song, Hong Sik Lee, Sang Woo Lee, Soon Ho Um, Jai Hyun Choi, Ho Sang Ryu
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):29-32. Published online June 30, 2009
- 524 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic resection is a standard curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) although only 10~30% of patients are indicated due to advanced stage or poor hepatic reserve. Five year survival rate after resection was reported as a mean of 55% (25~93%), but cases of early recurrence after hepatic resection had poor prognosis. As early recurrence after hepatic resection is the one of the most important factors that determines the prognosis, many investigators have been trying to determine the factors associated with early recurrence. We report a case of early multiple recurrence of HCC after curative hepatic resection probably due to microvascular invasion of tumor and too close resection margin. We would like to suggest that additional prophylactic measures need to be sought in this group of patients because these factors may influence on early recurrence.

- A Case of Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated by Hepatic Resection, which did not Respond to Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Jeong Han Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Seung Young Kim, Jae Hong Ahn, Ji Hoon Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Seung Hwa Lee, Hwan Hoon Chung, Tae Jin Song, Hong Sik Lee, Sang Woo Lee, Jai Hyun Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):63-66. Published online June 30, 2009
- 590 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Surgical resection is the treatment of choice for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in non-cirrhotic patients. The optimal indication for resection is a single tumor in a suitable location for resection. However, limit of the tumor size is not clear. We report a case of successful hepatic resection in patients with massive HCC sized more than 15 cm that did not respond to transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A 49-year-old male patient had received TACE two times for massive HCC. However, the tumor size increased. Right hemihepatectomy was performed despite the extensive tumor size and underlying liver cirrhosis. Ascites and wound infection were developed after resection, but the patient’s general condition got recovered soon. Until 6 months after surgery, recurrence has not been detected. However, distant metastasis was noted at 7th month. Although recurrence with distant metastasis was noted, we think aggressive surgical approach prolonged this patient’s survival.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Invasion
- Yeon Seok Seo, Beom Jin Park, Yun Hwan Kim, Soon Ho Um
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):69-73. Published online June 30, 2008
- 574 Views
- 13 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cholestatic type hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), in which obstructive jaundice is presented as the initial presentation of HCC, is rare. The prognosis of cholestatic type HCC is generally poor and most of the patients die from cholangitis or sepsis. Although some authors reported cases of successfully treated cholestatic type HCC with surgical resection, most of the patients are inoperable at the time of diagnosis. Several reports suggested that transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) showed a beneficial effect in improving the survival time and therefore, TACE should be tried as a first choice of therapy in patients with cholestatic HCC with sufficient liver reserve function. We experienced a case of obstructive jaundice as the initial presentation of HCC. His obstructive jaundice showed significant improvement after several sessions of TACE.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Combined Treatment
- Eun Sun Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyun Chul Kim, Yun Hwan Kim, Soon Ho Um
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):111-114. Published online June 30, 2008
- 481 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive tumor that frequently occurs in the setting of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. It is typically diagnosed late in the course of chronic liver disease, with the median survival following diagnosis of approximately 6 to 20 months. Although the mainstay of therapy is surgical resection, several other treatment modalities may also have a role. The patient’s hepatic reserve often dictates therapeutic options. Treatment options are divided into surgical therapies (i.e., resection, cryoablation, and orthotopic liver transplantation), and nonsurgical therapies (i.e., percutaneous ethanol injection, radiofrequency ablation, transarterial chemoembolization, systemic chemotherapy, or radiotherapy). Here we report a case of successfully treated HCC with combined therapy of surgical and nonsurgical modalities.

- Metastatic HCC Developed in the Peritoneal Cavity after Hepatic Resection - A Case Diagnosed by PET
- Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Jung Woo Choi, Yang Seok Chae, Won Hyeok Choi, So Young Kwin, Chang Hong Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2006;6(1):77-82. Published online June 30, 2006
- 456 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Positron emission tomography (PET) can detect tumor by estimation of glucose metabolism of tumor cells. We experienced the case of intraperitoneal metastatic hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC) diagnosed by PET. 36 year-old male patient had undergone hepatic resection for HCC. In the course of postoperative follow up, AFP level had risen gradually. We checked the abdominal sonography, CT, and celiac angiography, but results were unrevealing. To investigate hidden metastatic tumor, PET was performed and small tumor on the side of spleen was detected. The tumor was removed by laparoscopic operation, and revealed as HCC. AFP level gradually returned to normal.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter